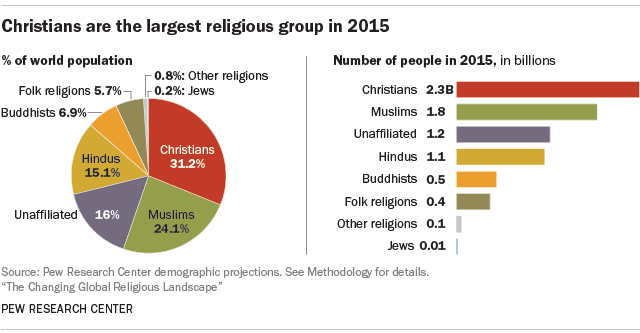
Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism are the three largest religions in the world. They have a long history, lots of people following them, and have greatly influenced different cultures. Christianity is the biggest, with more than 2.3 billion people following it. Islam comes next with about 1.9 billion followers. Hinduism is third, with around 1.2 billion people following it. These religions show how varied and rich human beliefs and practices can be, affecting how societies and people live and think all over the world.
Origins and Founders of the Largest Religions in the World
Christianity began with the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, who lived about 2,000 years ago in a place called Palestine. Christians believe that Jesus is the Son of God and was the special leader promised in earlier sacred writings. They follow his teachings and believe in the amazing things he did, his death, and his coming back to life, which are central to their faith.
Islam started in the 7th century, in a place called the Arabian Peninsula, with messages given to the Prophet Muhammad. Muslims think of Muhammad as the last in a long line of special messengers from God, which includes well-known figures like Adam, Abraham, Moses, and Jesus. They believe God’s messages to Muhammad were delivered by the angel Gabriel and later written down in the Quran, which is the sacred book of Islam.
Hinduism is a very old religion that didn’t start with one person or a single event. It grew slowly over many years, bringing together different ways of thinking, ceremonies, and customs from many cultures in the Indian subcontinent. It has many sacred writings like the Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita, and Puranas, and is filled with a wide variety of stories, legends, and deep teachings.
Beliefs and Practices of Christianity
Christianity is known for a few key beliefs, like the Trinity, which means God is seen as three distinct parts – the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit – but all one God. Christians also believe that Jesus is divine and that by having faith in him, people can be saved. This idea of the Trinity is a big part of how Christians understand God and how God connects with people.
At the heart of Christian belief is the idea that Jesus Christ is the Son of God and the one who saves people. Christians believe that Jesus made up for all human wrongdoings through his death and coming back to life. They think this act gives people the chance for eternal life if they trust in him. This key belief shapes Christian faith and is shown in their ceremonies and special rituals, like baptism and the Eucharist (also known as Holy Communion), where they come together to remember and honor what Jesus did.
Christian activities include worshipping, praying, and taking part in church ceremonies and special rituals called sacraments. Christians often come together for group worship services. During these services, they pray, sing hymns, listen to readings from the Bible, and hear talks given by church leaders or clergy. Sacraments like baptism and the Eucharist are very important to them because they are seen as visible signs of God’s grace and a way to refresh their spiritual lives.
Spread and Distribution of Christianity
Christianity grew from its simple beginnings in the ancient Near East to become the largest religion in the world, showing its lasting attraction and big impact. The early Christian movement spread throughout the Roman Empire and further, helped by the work of Jesus’ followers and apostles. This happened even though there were times when Christians faced persecution and resistance.
Important moments like the conversion of Emperor Constantine to Christianity in the 4th century, and the Roman Empire later making Christianity its official religion, played a big role in Christianity becoming more widespread. Throughout the Middle Ages, the efforts of saints, religious scholars, and groups of monks to spread Christianity helped it grow even more. This growth continued into the early modern period, with the age of exploration and colonization helping to spread Christianity around the world.
Nowadays, Christianity has followers all over the world, across different continents, cultures, and groups of people. It has a strong presence in places like the Americas, Europe, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Oceania. Also, Christianity is gaining more followers in Asia, especially in countries such as South Korea, China, and the Philippines.
Denominations and Sects within Christianity
Christianity includes many different groups, branches, and ways of thinking, each with its own set of beliefs, ways of worshiping, and church organization. Over time, as Christianity has grown and changed, it has split into various denominations and affiliations. This has led to a rich variety of theological ideas and has made the Christian religious scene very diverse.
Catholicism, which is the biggest branch of Christianity, connects itself back to the early Christian Church and the special role of the Bishop of Rome, who is also known as the Pope. In Catholicism, there’s a strong focus on the importance of sacred traditions, the guidance of the Magisterium (which is the church’s authority on teaching), and the church’s sacraments, like the Eucharist celebration and showing honor to saints.
Protestantism started in the 16th century with the Protestant Reformation, a movement that questioned the Roman Catholic Church’s power and called for changes. These changes were to base beliefs and practices solely on the Bible (sola scriptura), to emphasize that faith alone (sola fide) is needed for salvation, and to highlight the importance of grace alone (sola gratia). Protestantism includes many different groups, like Lutherans, Calvinists, Anglicans, Baptists, Methodists, and also evangelical and Pentecostal churches.
Eastern Orthodoxy is part of the Eastern Christian tradition, going back to the early Christian Church in the Byzantine Empire and important meetings like the councils of Nicaea, Constantinople, and Chalcedon. It focuses on ceremonial worship, a mystical approach to faith, and keeping the traditions from the apostles through seven sacraments and the teachings from the major church gatherings known as the Ecumenical Councils.
Islam Beliefs and Pillars of Faith
Islam, which is the world’s second-largest religion, has a few key beliefs and practices at its heart, called the Five Pillars of Islam. These pillars are like the base of Muslim faith, helping followers in their spiritual growth and everyday actions.
- Shahada: The Shahada, or Declaration of Faith, is the very first important rule of Islam. It’s a special sentence that people say to show they follow Islam: “There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is his messenger.” When someone says this sentence with true belief, it means they really believe that Allah is the only God and Muhammad is his messenger.
- Salat: Salat, or Prayer, is the second key rule of Islam. Muslims pray five times a day at specific times. These prayers help Muslims feel close to Allah, ask for help, and say thank you. During Salat, there are special movements like bowing and kneeling, and Muslims also say verses from their holy book, the Quran.
- Zakat: Zakat, or Charity, is the third important rule in Islam. It’s about giving to help others. Muslims give a part of what they have, usually 2.5% of their money and things they own, to help people who don’t have much. This helps everyone in the community feel supported and taken care of.
- Sawm: Sawm, or Fasting during Ramadan, is the fourth key practice in Islam. In the special month of Ramadan, Muslims don’t eat or drink from sunrise to sunset. This helps them practice self-control, feel what it’s like for people who are less fortunate, and clean their hearts and minds. Fasting is also a time to feel closer to Allah and ask for forgiveness for any mistakes made in the past.
- Haji: Hajj, or the Pilgrimage to Mecca, is the fifth main rule of Islam. It’s a special trip to the holy city of Mecca that Muslims should try to make at least once if they are healthy enough and can afford it. This trip happens every year in a month called Dhu al-Hijjah. During Hajj, Muslims do special actions and prayers that remember the stories of Prophet Abraham and his family.
The Five Pillars of Islam are basic rules and practices that show what being Muslim is all about. They help guide how Muslims live, making them better people and bringing them closer together. These pillars are like a foundation that supports the growth of their faith, how they act in a good way, and how they support and care for each other.
Global Distribution of Islam
Islam started in the Arabian Peninsula and has grown to become one of the biggest religions around the world. This spread happened for many reasons, like trade, taking over lands, people moving to new places, and efforts to share the religion with others. Now, Islam is practiced in many different countries and areas, making it a religion with a rich variety of cultures and traditions.
The Middle East is where Islam began and is still a key center for Islamic culture and religion today. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, Egypt, and Turkey have been very important in developing Islamic beliefs, ways of worship, and rules for society. Two cities in Saudi Arabia, Mecca and Medina, are especially sacred in Islam. Every year, millions of Muslims go on a special religious trip, called the Hajj, to visit these cities.
North Africa has a strong Islamic heritage, with countries such as Egypt, Morocco, and Algeria showing a long history of Islamic leadership, beautiful buildings, and learning. Its position next to the Mediterranean Sea helped a lot with trade and the sharing of ideas between Muslim areas and Europe, helping to spread Islamic culture and traditions.
South Asia is home to a large number of Muslims, especially in countries like Indonesia, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, which are among the countries with the most Muslims in the world. Indonesia stands out because it has the highest number of Muslims of any country. In Indonesia, Islam plays a big role in how people live, in society, and in politics.
Southeast Asia, which includes countries like Malaysia, Brunei, and parts of the Philippines, has a notable Muslim community. This is largely due to the area’s history of trade and interaction with other Muslim regions. You can see the impact of Islam in the beautiful buildings, delicious food, and various cultural traditions across these diverse societies, showing the deep roots of Islamic influence over many years.
Islam has also grown and spread to areas beyond its original centers, like Europe, North America, and Sub-Saharan Africa. This expansion is due to people moving to new places, others choosing to follow Islam, and communities of Muslims living far from their original homes. As a result, Islam’s influence is becoming more varied worldwide, with Muslims actively participating in different aspects of life in the societies where they live.
Islamic Sects and Schools of Thought
Islam includes a variety of groups and ways of thinking, each offering its own take on Islamic teachings, laws, and spiritual activities. These differences have developed over time due to disagreements in beliefs, historical events, and the social settings of different communities. This has led to a rich tapestry of beliefs and practices within the broader Islamic faith.
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam, with most Muslims around the world being Sunnis. They follow the teachings of Prophet Muhammad, the Quran, the agreed-upon views of the first Muslim community, and the interpretations of Islamic scholars. Sunni legal thought is guided by four main schools: Hanafi, Maliki, Shafi’i, and Hanbali. Each school has its own way of understanding and applying Islamic laws.
Shia Islam is the second major branch of Islam. Shias believe in a special kind of leadership called the imamate, which means they follow leaders (imams) who they believe are chosen successors from Prophet Muhammad’s family. Shias see Ali ibn Abi Talib, the Prophet’s cousin and son-in-law, and Ali’s descendants as the true leaders of Muslims. Within Shia Islam, there are different groups, with Twelver Shia being the biggest, and others like Ismaili and Zaidi Shias also being significant.
Sufism, also known as Islamic mysticism, emphasizes the inward journey of the soul towards God (Allah) through spiritual practices such as meditation, dhikr (remembrance of God), and self-discipline. Sufis seek to attain spiritual enlightenment and union with the Divine by purifying the heart and cultivating qualities of love, compassion, and humility. Sufism transcends sectarian divisions and has historically influenced Islamic spirituality and culture across Sunni and Shia communities.
Comparative Analysis of the Three Largest Religions
Analyzing Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism offers insights into their beliefs, practices, and cultural impacts, highlighting both commonalities and differences.
- Beliefs About God:
- Christianity centers on the Trinity: God as Father, Son (Jesus Christ), and Holy Spirit, emphasizing Jesus’s divinity and the Holy Spirit’s guidance.
- Islam stresses the absolute oneness of Allah, rejecting the Trinity, and focusing on Allah’s unity and transcendence.
- Hinduism presents a spectrum from monotheism to polytheism, with some viewing the divine as a single supreme entity and others worshiping multiple gods.
- Beliefs About the Afterlife:
- Christians believe in resurrection, heaven, hell, and, in some traditions, purgatory, with eternal destiny hinging on faith in Christ.
- Muslims anticipate a Day of Judgment leading to paradise or hell based on deeds and faithfulness to Islamic principles.
- Hindus embrace concepts like reincarnation and karma, aiming for moksha, or liberation from the cycle of rebirth, to reunite with the divine.
- Moral Values and Ethical Principles:
- Christian ethics focus on love, compassion, and living virtuously based on Jesus’s teachings and the Ten Commandments.
- Islamic ethics draw from the Quran and Hadith, advocating justice, mercy, and adherence to Sharia, guiding personal and communal conduct.
- Hindu ethics revolve around dharma, emphasizing moral duty, righteousness, and virtues like honesty and compassion, guided by sacred texts.
- Role of Religious Practices:
- Christian practices include prayer, sacraments, and community worship to foster a relationship with God and spiritual growth.
- Islamic practices are structured around the Five Pillars, establishing a framework for worship and ethical living.
- Hindu practices vary widely, encompassing rituals, temple worship, and festivals, reflecting the religion’s diversity and inclusivity.
- Interfaith Dialogue and Understanding:
- Christianity promotes dialogue to foster respect and unity among different denominations and religions.
- Islam encourages respectful engagement with other faiths, aiming for mutual understanding and cooperation.
- Hinduism values the universality of spiritual truths, engaging in dialogue to celebrate diversity and promote harmony.
- Cultural and Social Impact:
- Christianity’s legacy is evident in art, literature, social institutions, and politics, shaping Western culture and beyond.
- Islam’s contributions span art, science, education, and governance, influencing cultures across historical Islamic empires.
- Hinduism has deeply influenced art, literature, and social structures, particularly in South Asia, enriching global culture.
These comparisons illuminate the unique aspects and shared values across these religions, contributing to a deeper understanding of their roles in human history and society.
Challenges and Controversies in the Largest Religions in the World
All big religions like Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism have made great contributions to the world but also face tough challenges today. Understanding these issues helps us see how complex religion’s role in society is and highlights the need for open conversations and coming together.
Christianity
In our diverse world, Christians are learning how to live and interact with people from other religions. This calls for efforts to understand each other better and live peacefully together.
Christians are discussing how to handle big social issues like equality, environmental care, and human rights. Different views on topics like LGBTQ+ rights and abortion show the variety of opinions in the community.
Scandals involving some church leaders have hurt people’s trust in the church. This has led to calls for the church to be more open, responsible, and to make positive changes.
Islam
Sadly, some violent groups misuse Islam’s name to justify their actions. Fighting this problem means tackling the reasons people join these groups and correcting misunderstandings about Islam.
Differences and conflicts between various Muslim groups can cause division. Working towards peace and understanding within the Muslim community is crucial.
Prejudice and unfair treatment of Muslims is a big problem. Fighting Islamophobia involves educating people, speaking up against stereotypes, and standing together across different communities.
Hinduism
Hinduism is working to overcome the old caste system that led to unfair treatment of certain groups. While progress has been made, there’s still work to do in achieving true equality.
In areas with a mix of religions, tensions can lead to conflicts. Promoting peace and understanding between different religious groups is important for everyone’s well-being.
Hinduism teaches respect for nature, but modern challenges like pollution and climate change are big threats. Encouraging care for the environment and sustainable living is key for the planet’s future.
Understanding and addressing these issues is important for the growth and harmony of these religious communities and society as a whole.
Future Trends in Major Religions
As the world changes, so do major religions like Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism. Understanding the future trends helps us see what challenges and opportunities these religions might face and how they can work together for a better world.
With the world becoming more connected, Christians will interact more with different cultures and beliefs. This will lead to more conversations and joint efforts with other religions on big issues like human rights and taking care of the planet.
In places where more people are questioning traditional beliefs and the role of religious institutions, Christianity might see changes. There could be new ways of understanding faith, more focus on personal spirituality, and increased social action.
Christians might become more involved in social issues, pushing for fairness, kindness, and making a positive impact in their communities and beyond.
Young Muslims are likely to take on bigger roles in shaping Islam’s future. They might bring new ideas, work towards fairness and rights, and find fresh ways to express their faith and lead.
There will be efforts to bring different Muslim groups closer together. Through dialogue and cooperation, there’s a hope to overcome differences and work unitedly on common goals.
As Muslims encounter new global challenges, they’ll find ways to blend Islamic teachings with modern life, ensuring their traditions stay relevant while also fitting into the wider world.
As Hindus live in more parts of the world, they’ll continue to balance keeping their traditions with adapting to new environments. This includes being part of a global community while staying true to Hindu values.
Hinduism’s deep respect for nature will inspire more Hindus to fight for a healthier planet. They’ll join others in tackling environmental problems like climate change and pollution.
Hinduism will emphasize peace and working together with different religions. Through interfaith projects, Hindus will seek to solve common problems, help those in need, and build understanding across diverse communities.
These trends point to a future where major religions adapt, engage more with global issues, and find new ways to contribute positively to the world and their followers’ lives.
Conclusion
To wrap it up, the big three religions – Christianity, Islam, and Hinduism – have a long history and a big influence on people and places all over the world. Even though they face tough problems like keeping up with modern life, making tough choices, and getting along within and outside their groups, they keep changing and growing.
Looking forward, they are ready to handle the challenges of a connected world, work with all kinds of people, and help solve big world problems by talking things out, making changes, and taking action. The future looks like these religions will work together more, pay more attention to what young people and new ideas can bring, and really work hard to make the environment better and treat everyone fairly. Getting to know these changes is important for everyone to get along better, find peace, and share good values in our world that’s more connected every day.